Eating Alkaline
Alkaline Eating is so basic 🙄 Ha, Literally! And our bodies actually perfect this pH, this alkalinity to an acidic environment. I mean, wouldn’t you too? Wake up and your day starts with acid rain… sounds like a case of the Mondays and i’m going back to bed.
But in all seriousness "alkaline eating" has been gaining popularity in recent years for good reason. It can improve our overall health and prevent disease. Let’s dive in.
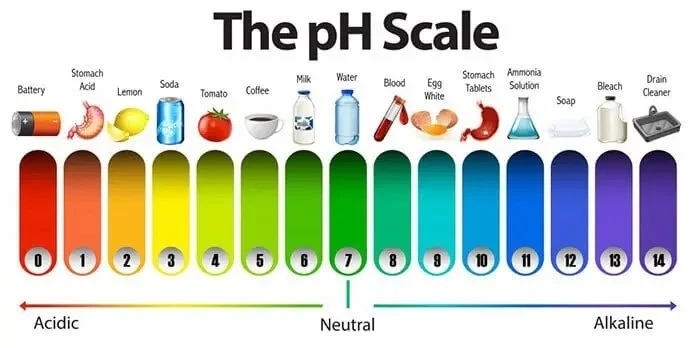
To understand the benefits of alkaline eating, it's important to first understand what it means for the body to be alkaline or acidic. The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most alkaline. Our body works to maintain a slightly alkaline pH between 7.365 - 7.45 which is not only optimal but crucial for proper bodily function (we’ll expand on that in more detail later) it’s also the pH where healing can take place. If the body gets acidic, below 7.3 thats when troubles starts. pH at 6.8 is where symptoms can occur and 5.8 is where cancers can begin to form. If the pH drops below 3.5, you’re headed to the hospital cuz the human body can not sustain life. Today’s modern lifestyle pose factors that can directly effect the bodies ideal pH range including; diet, stress, and environmental toxins which can cause the body to become more acidic, disrupting the balance.
What does the pH do?
pH indicates the level of H+ ions, where low pH indicates too many H+ ions and high pH indicates too many OH- ions. Simple biology right. In the body, different body fluids have different functions and thus different pH values. For example, the pH of saliva ranges from 6.5 to 7.5. After swallowing, food reaches the stomach where upper and lower parts of stomach have different pH values. The upper part has a pH of 4−6.5, while the lower part is highly acidic with a pH of 1.5−4.0. Moving along into the intestine, we neutralize with a slightly alkaline pH of 7−8.5.
Every cellular process, including metabolism, membrane potential, cellular growth and proliferation, movement of substances across membranes, polymerization of the cytoskeleton are all affected by changes in intracellular pH [s]. So maintaining the pH values of different regions is critical for their function and different cells developed different mechanisms for regulating intracellular pH [s]. When the pH balance is off, enzymes that are normally constructive can become destructive, and vice versa. For example, if you’re stomach didn’t have enough hydrogen (Hydrochloric Acid), the enzyme pepsin would be unable to act to break down the food, leading to heartburn and indigestion. Beta cells (located in the pancreas responsible for making insulin, the endocrine hormone that controls blood glucose levels) are especially sensitive to pH and cannot survive if the body is too acidic which inhibits our ability to regulate blood sugar levels appropriately. The system most effected by alterations in acid-base balance are oxygen delivery. A decrease in pH means a decreased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen [s]. Oxygen is essential for ATP {energy) generation through oxidative phosphorylation, and therefore must be reliably delivered to all metabolically active cells in the body [s]. If bloods isn’t transporting oxygen efficiently, then body systems aren’t making the energy they need to sustain life.
The body is continually striving to achieve a balanced pH level (aka cellular homeostasis) and it needs both alkaline and acidic elements in the right ratios in the right regions to create positive and negative charges. This charge creates a steady pulses of electrical energy, which does lots of things but mostly pump ion into and out of cells creating a buffer.
How is pH Regulated?
Maintaining the Body acid-base balance
There are primarily three mechanisms: buffer systems, respiratory (breathing) and renal (kidney) control.
Buffering Systems
The regulation of pH is achieved through the actions of sodium and hydrogen Na+–H+ ion exchangers (aka sodium–proton exchanger) and other pumps. Changes in intracellular pH are a cell’s response to externally applied agents, such as hormones, growth factors, and others. This buffering system is extremely efficient, with different systems work at different rates. It takes only seconds for the chemical buffers in the blood to make adjustments to pH.
A buffer is a substance that prevents a radical change in fluid pH by absorbing excess hydrogen or hydroxyl ions. Most commonly, the substance that absorbs the ion is either a weak acid, which takes up a hydroxyl ion (OH–), or a weak base, which takes up a hydrogen ion (H+). Several substances serve as buffers in the body, including cell and plasma proteins (2/3 all buffers), hemoglobin, phosphates, bicarbonate ions, and carbonic acid[s].
Respiratory System:
The respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that help you breathe. It includes your airways, lungs and blood vessels. In active tissues, there is an increase in hydrogen ions. These can react with bicarbonate in the red blood cells to form carbon dioxide which can then be exhaled by the lungs. We release carbon dioxide from the body when you exhale and the body regulates body pH by altering the respiratory rate (frequency of breath). More breaths mean more carbon dioxide being released and neutralizing the acidity (raising your pH)[s]. This system works quite quickly to repair the acid-base balance, in fact “doubling the respiratory rate for less than 1 minute, removing “extra” CO2, would increase the blood pH by 0.2 [s]”. Pretty Awesome! I wonder if reading this has prompted you to take a deep breath?
Kidney / Urinary Secretions
The kidneys maintain normal acid-base balance primarily through the reabsorption of sodium or bicarbonate and excreting acids (hydrogen and ammonium ions) via the tubular section. This process is known as “compensation.” As the body, or urine become increasingly acidic, the amount of sodium and excess acid retained by the body decreases. If bicarbonate is reabsorbed and/or acid is secreted into the urine, the pH becomes more alkaline (increases). On the later, renal compensation for an overly alkaline state involves a decrease in HCO3 – reabsorption. When bicarbonate is not reabsorbed or acid is not excreted into the urine, pH becomes more acidic. Secretion of an acid or alkaline urine by the kidneys is one of the most important mechanisms the body uses to maintain a constant body pH [s] and this metabolic compensation takes longer to occur: days rather than minutes or hours as in breathing [s].
There exist many factors too that can interfere with this regulation system. For instance a decrease of blood bicarbonate {acidosis) can result from the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase by certain diuretics or from excessive bicarbonate loss due to diarrhea. Blood bicarbonate levels are also typically lower in people who have Addison’s disease (chronic adrenal insufficiency), in which aldosterone levels are reduced, and in people who have renal damage, such as chronic nephritis. Finally, low bicarbonate blood levels can result from elevated levels of ketones (common in unmanaged diabetes mellitus), which bind bicarbonate in the filtrate and prevent its conservation.
What does an Acidic Body feel like:
Even though our bodies are well apt to maintaining a balance, however will all things, too much can inevitably too much for the body to handle. When our bodies are too acidic it could lead to a number of health complications. For example, an acidic environment can promote inflammation, weakening our immune system, making us more susceptible to illness and infection. I can cause damage to our cells and can even lead to arrhythmias and seizures. Even leading to chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. A pH of 6.8 is when disease and symptoms can begin. Some early warning signs of imbalance include; allergies, breathing disorders, chronic colds and flus, headaches, indigestion, inflammation, fatigue, muscle cramping, pain, skin troubles and sinus problems[s].
As acid continues to accumulate in the body, several organs and glands become effected including your thyroid, adrenal glands and liver. Excess acidity forces the body to borrow minerals from other reserves stored in our bodies. This includes calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium from vital organs, bones, and teeth to buffer (neutralize) the acid and safely remove it from the body. As a result, the body can suffer severe and prolonged corrosion due to high acidity, a condition that may go undetected for years. Acidosis leads to serious problems with major organs such as the liver, heart, or kidneys [s].
How does is get Acidic
Changes in pH can occur from prolonged dietary choices (see the list below of highly acidic foods) but it can also be a warning sign that something else is a miss. If you are in a constant state of stress, overly secreting stress hormones. Chronic stress also leads to shallow breathing or even breath holding. Without proper respiratory countermeasures to combat acidity, body levels will rise. If you have a high toxic load, Pesticides and other chemicals, heavy metals; industrial pollutants; hormones and antibiotics/chemicals found in foods, plastics, cleaning supplies and beauty products; and even potential chemicals in your tap water all could increase acidity in the body. A diet that is primarily Acidic Diet meaning that you are mostly consuming sugar, refined flours, food additives, table salt, trans fats, fried foods, meat, dairy, alcohol, soda and caffeine. What the body takes in directly makes it difficult for your body to restore its pH balance.
Changes in your normal blood pH might be a sign of certain health conditions and medical emergencies; asthma, diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, lung disease, gout, infection, shock, hemorrhage (bleeding), drug overdose and/or poisoning.
Testing your PH
There exist a couple methods to see how your body measures up on a pH scale. The quickest and easiest is by measuring you urinary pH. Urine pH litmus paper will not show exact blood pH levels, but it will help to show if something is off-balance. Ideal urine reading should be between 6.5 to 7.5.
There are also at-home blood finger-prick test strips are also available but require a unit for reading and there is no promise that it will be as accurate as a blood pH test at your doctor’s office.
I’m Don’t share all this information for general knowledge, I share to empower you with ability to do something about it. I empower you to take ownership of your health. I share because I care and I want you to know that there is something that you can do, starting today that can have a tremendous impact on your overall health.
Lets Get Alkaline!
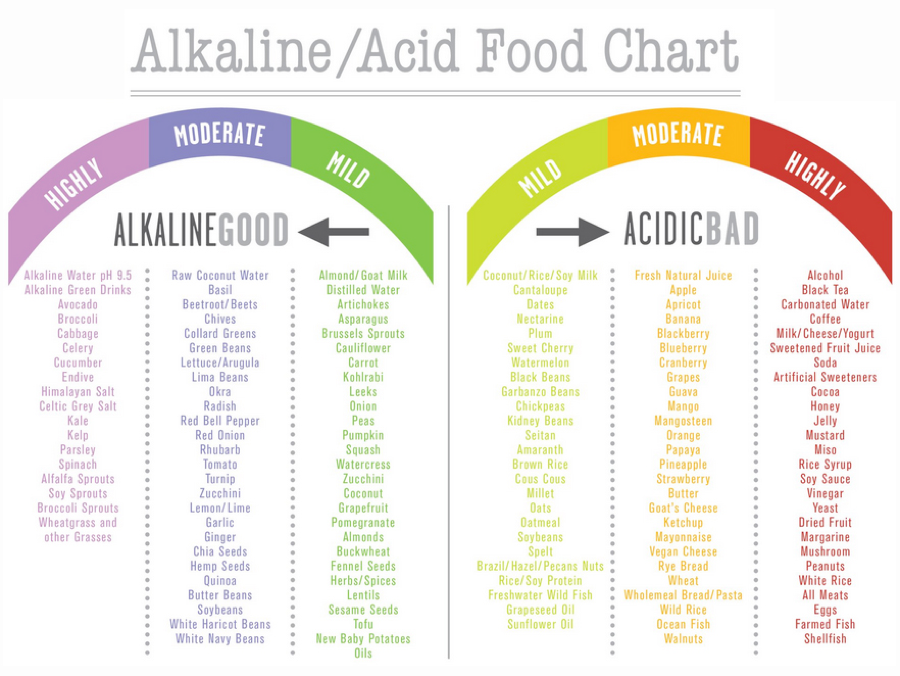
So, what can we do to promote alkalinity in the body and reap the benefits of a happy internal environment? The biggest factor/impact is in what out we expose our bodies to on a repeated basis. I’m talking about those daily dietary choices. Should you want to tip the scale towards alkalinity then one must consume a diet rich in alkaline-promoting foods. These are fruits and vegetables (especially leafy greens), nuts and seeds, beans and herbs (refer to the chart below). On the other hand, highly processed and refined foods, animal products, and sugar are all highly acidic and can contribute to an acidic environment in the body.
Some easy ways to add more alkalining elements into your day to day:
Drinking cup of water with a squeeze of lemon first thing in the morning.
Choose leaner cuts of meat and plenty of variety. For example, maybe red meat once a week, eggs three times a week, chicken or turkey breast two times a week, and fish (also high in omega-3s) two - three times a week.
Choose portions of brown rice and other whole grains well.
Swapping a green leafy vegetable over a starchy vegetable or complex carbohydrates during meals because they also have carbohydrates too.
Adding alkalizing supplements such as chlorella, digestive enzymes, bromelain, essential fatty acids, a high quality multivitamin and B complex.
Making simple changes your diet to include about 75-80 percent alkaline foods, you won’t need to test your pH. You’ll feel the effects of improved energy level, better sleep, and increased vitality will tell you it’s working!
While adding is easy, avoiding is often the hardest parts. But I know when there is a will, there is a way. If you would like to improve your body pH, then there are some foods that should only be chosen “on occasion.” Consuming no more than 20% of the following as they surly make the body more acidic:
Dairy products like cheese, milk, yogurt and ice cream.
Wheat and Gluten products
Refined grains and simple carbohydrates such as white rice, white bread, pasta
Processed products, such as chips, snacks, hot dogs, cold cuts, and frozen meals.
Alcohol
Artificial sweeteners
Excessive caffeine (especially coffee can be highly acidic)
Sugary treats, including soda, candy and
Tabaco
What Else / Lifestyle
In addition to consuming more alkaline-promoting foods, other lifestyle choices exist that can contribute to a more alkaline body. Getting enough rest, managing stress daily, and staying hydrated are all important for maintaining a healthy pH balance.
Use the Power in your Breath
The deeper you breathe, the more alkalising is the effect on your body[s]. By just taking five deep breathes, you put more oxygen in your system, which in turn helps clean your system out! Remember, the less the CO2 in our system, the less acidic your body will be. To ensure they are deep, when you breath put on hand on our tummy. The breath should force your tummy to inflate (the hand move outward) and not make your shoulders rise. If you like, start by counting to 4 on your inhale, hold for 4 seconds, then exhale to the count of 6 seconds.
Manage Stress
Stress creates cellular acidity by triggering cortisol, a powerful catabolic hormone that makes the body more acidic. Stress is often accompanied with shallow breathing. Taking steps to bringing yourself back into balance could include: Creating restorative rituals that make you feel good and balance your mind-body connection; Spending time in nature as often as possible; Going to bed early; Meditate; Taking baths; Journal; Go for a walk after dinner; Or Do whatever it is that makes you feel centered and more at peace.
Prioritize Sleep
During our rest cycles the body is able to fully rest and restore itself. Allowing time to regenerate and regain balance in our ph equilibrium. Our bodies need the deep, restorative sleep, which comes after 7-8 hours [s].
Hydrate
Our bodies are > 65% water and adequate water intake is necessary to support all body systems. It clears out excess toxins and gives your body a ph neutral medium with which to filter those ions. The recommendation is half your body weight in ounces daily to keep your body systems regulated. That means, if your weight is 130 pounds, drink 65 ounces. But I say for optimal; filtration to drink your body weight in ounces. You could carry a reusable bottle with you and fill it with filtered water all day.
Movement
Exercise regularly to actively move acids out of the body. Not just by allowing sweat to fuse out of your pores. The more we sweat, the more toxins we release. The fewer toxins in our systems, the less acidic our bodies will be. This could be a gym session or it could be simply walking in nature, dancing or running, even swimming are great at great ways to move the body. I have quite recently been enjoying restorative practices in yoga, also kundalini yoga, foam rolling and gentle stretching. Yoga is especially beneficial for alkalizing because it helps with flexibility and stress management, but also increases your practice of deep breathing.
Massage - DRy Brushing
Massage is a great stress reducer and some techniques can even help with lymphatic drainage. Which lymphatic drainage helps to stimulate your lymphatic system. which enhances circulation to improve the flow of blood and lymph to help remove acidic waste.
Why again?
Why do we want to be Alkaline, what are the benefits of alkaline eating? By promoting alkalinity in the body, we are loving our bodies and giving it the tools to perform at tits best. We are also potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases, boost our immune system, and even improving mood and mental health. Additionally, you’d be consuming a diet that is more rich in high nutritional value containing fruits and vegetables which are proven to have numerous health benefits, such as reducing inflammation, warding osteoporosis and improving digestion.
In conclusion, while the concept of alkaline eating may seem trendy, there is science to back up its potential benefits for our health. By consuming a diet rich in alkaline-promoting foods and adopting other healthy lifestyle habits, we can promote a more alkaline environment in our bodies and potentially reap numerous health benefits in the process.